Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kawasaki, Nobuchika; Watakabe, Tomoyoshi; Wakai, Takashi; Yamamoto, Tomohiko; Fukasawa, Tsuyoshi*; Okamura, Shigeki*
Proceedings of 2016 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2016) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2016/07
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors (SFRs) have components with thinner walls as compared with light water reactors, although Japan is an earthquake-prone country. Thus, seismic isolation systems have been conventionally employed in SFR system design to reduce seismic forces on the systems in Japan. Implementation of seismic design in the reactor core and buckling design in the reactor vessel requires 8 Hz (or less) vertical frequency's isolation system being applied. This paper introduces three isolation concepts to achieve the frequency. The isolation systems, which enable vertical 8 Hz natural frequency, comprise thicker laminated rubber bearings (TRBs). By combining coned disk springs with TRBs, vertical natural frequency is in a range from roughly 3 Hz to 5 Hz. Combining pneumatic springs to RBs and adding the rocking suppression system, vertical natural frequency becomes under 1 Hz. All isolation systems need horizontal damping like oil dampers. A vertical 8 Hz isolation system with TRBs and oil dampers is under development in Japan as a principal isolation concept. The reasons of choosing this system are its simplicity and the number of developing issues. Since TRBs and oil dampers are basic isolation elements, they can be applied to other isolation systems. The response acceleration of 5 Hz vertical isolation is 50% of that of 8 Hz based on the analytical survey. A series of static tests of coned disk springs was carried out to confirm design equations. Based on these knowledge, 5 Hz vertical isolation system with TRBs and the coned disk springs can be designed. The response acceleration of 1 Hz vertical isolation is 10% of that of 8 Hz. A rocking suppression system was studied in the past, and the further simplification of this system is the largest challenge for this concept. These three isolation concepts are isolation candidates for SFRs in Japan. To obtain enough seismic margins for each plant site, these isolation systems need to be developed.
Watakabe, Tomoyoshi; Yamamoto, Tomohiko; Fukasawa, Tsuyoshi*; Okamura, Shigeki*; Somaki, Takahiro*; Morobishi, Ryota*; Sakurai, Yu*; Kato, Koji*
Proceedings of 2016 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2016) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2016/07
A seismic isolation system composed of a thick rubber bearing and an oil damper has been developed for Sodium cooled Fast Reactor. One of the advantages of the isolation system is employing the thick rubber bearing in order to realize the longer vertical natural period of a plant, and it leads to mitigation of seismic loads to mechanical components. Rubber bearing technology has progressed based on many past studies, but test data regarding an aging effect is not enough. Also, there is no data of linear strain limit and breaking behavior for the thick rubber bearing after aging. This paper focuses on aging properties of the thick rubber bearing, such as basic mechanical properties and ultimate strength. An aging promote test of the thick rubber bearing was performed by using 1/2 scale and 1/8 scale rubber bearings. Aging of the rubber bearing was reproduced by thermal degradation, where the target aging period was 30 years and 60 years. The load deflection curves of the thick rubber bearing after aging were obtained through the horizontal and vertical static loading tests, and the aging effect was evaluated by comparing with the initial mechanical properties.
Yamaguchi, Yoshihito; Katsuyama, Jinya; Li, Y.
Proceedings of 2016 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2016) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2016/07
Azuma, Kisaburo*; Li, Y.; Hasegawa, Kunio; Shim, D. J.*
Proceedings of 2016 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2016) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2016/07
Azuma, Kisaburo*; Li, Y.; Hasegawa, Kunio
Proceedings of 2016 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2016) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2016/07
Lu, K.; Katsuyama, Jinya; Li, Y.; Iwamatsu, Fuminori*
Proceedings of 2016 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2016) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2016/07
Stress intensity factor (SIF) solutions for subsurface flaws near the free surface in plates were numerically investigated based on the finite element analyses. The flaws with aspect ratios 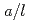 = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4 and 0.5, the normalized ratios
= 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4 and 0.5, the normalized ratios 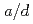 = 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 and 0.8 and
= 0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6 and 0.8 and 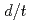 = 0.01 and 0.1 were taken into account, where a is the half flaw depth, l is the flaw length,
= 0.01 and 0.1 were taken into account, where a is the half flaw depth, l is the flaw length,  is the distance from the center of the subsurface flaw to the nearest free surface and t is the wall thickness. Fourth-order polynomial stress distributions in the thickness direction were considered. In addition, probabilistic fracture mechanics analyses were also performed and some example solutions obtained in this work were used to evaluate the conditional probability of failure of a reactor pressure vessel under a pressurized thermal shock event. The results indicated that the numerical SIF solutions calculated in this study are effective in engineering applications.
is the distance from the center of the subsurface flaw to the nearest free surface and t is the wall thickness. Fourth-order polynomial stress distributions in the thickness direction were considered. In addition, probabilistic fracture mechanics analyses were also performed and some example solutions obtained in this work were used to evaluate the conditional probability of failure of a reactor pressure vessel under a pressurized thermal shock event. The results indicated that the numerical SIF solutions calculated in this study are effective in engineering applications.
Lu, K.; Li, Y.; Hasegawa, Kunio; Lacroix, V.*
Proceedings of 2016 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2016) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2016/07
Iwata, Keiko; Tobita, Toru; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Yoshimoto, Kentaro*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of 2016 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2016) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2016/07
The effect of warm pre-stressing (WPS) on fracture toughness was evaluated for a reactor pressure vessel steel. Various types of thermomechanical loadings were applied to 1T-CT specimens. The results were compared with predictions from several analytical WPS engineering models. The specimen size effect was subsequently investigated under the load-unload-cool-fracture transient condition using 1T-, 0.4T-, and 0.16T-CT specimens. Analyses of the plastic zone distribution and residual stress were conducted to identify the difference in the WPS effect among the specimens.
Lu, K.; Katsuyama, Jinya; Li, Y.
Proceedings of 2016 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2016) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2016/07
Fukasawa, Tsuyoshi*; Okamura, Shigeki*; Yamamoto, Tomohiko; Kawasaki, Nobuchika; Hirotani, Tsutomu*; Moriizumi, Eriko*; Sakurai, Yu*; Masaki, Nobuo*
Proceedings of 2016 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2016) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2016/07
Half-scale thick rubber bearing to investigate ultimate properties application for a Sodium-cooled-Fast-Reactor. The fundamental restoring-force characteristics of the thick rubber bearings has been already cleared through the static loading tests using a half-scale thick rubber bearing, 800 mm in diameter. However, variations of the restoring force characteristics and ultimate properties have not been obtained yet. The purpose of this paper is to indicate the variation of the stiffness and damping ratio concerning restoring force characteristics and the breaking strain or stress as ultimate properties through static loading tests using the half-scale thick rubber bearings.
Uno, Shumpei; Katsuyama, Jinya; Watanabe, Tadashi*; Li, Y.
Proceedings of 2016 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2016) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2016/07
For structural integrity assessment on reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) of pressurized water reactor during the pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events, thermal history of coolant water and heat transfer coefficient between coolant water and RPV are dominant factors. These values can be determined on the basis of thermal-hydraulics (TH) analyses simulating PTS events and Jackson-Fewster correlation. Using these values, subsequently, loading conditions for structural integrity assessments of RPVs are evaluated by structural analyses. Nowadays, three-dimensional TH and structural analyses are recognized as precise assessment method for structural integrity of RPVs. In this study, we performed the TH and structural analyses using three-dimensional models of cold-leg, downcomer and RPV in order to evaluate loading conditions during a PTS event more accurately. Distributions of temperature of coolant water and heat transfer coefficient on the surface of RPV were calculated by TH analysis. Loading condition evaluation was then performed by using these values and taking the weld residual stress due to weld-overlay cladding and post-weld heat treatment into consideration. From these analyses, we obtained histories and distributions of loading conditions at the reactor core region of RPV. We discussed the conservativeness of current structural integrity assessment method of RPV prescribed in the current codes through the comparison in the loading conditions due to PTS event.
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of 2016 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2016) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2016/07
It has been accepted that neutron irradiation embrittlement of reactor pressure vessel is caused by irradiation-induced formation of solute clusters (SCs) and matrix damages (MDs). In the present study, to analyze the contribution of chemical composition contained in SCs to irradiation embrittlement at high fluence region, statistical analysis using the Bayesian nonparametric (BNP) method was performed for Japanese PWR surveillance data. The significance of P, Si and Mn contents, which are not necessarily included in embrittlement correlations unlike the Cu and Ni content, was evaluated. The BNP method can learn the complexity of the statistical model itself from the input data and infer the predicted data with individual probability distribution of predict condition. The result suggested that irradiation embrittlement was most affected by the Si content at high fluence region.
Ando, Masanori; Yada, Hiroki; Tsukimori, Kazuyuki; Ichimiya, Masakazu*; Anoda, Yoshinari*
Proceedings of 2016 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2016) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2016/07
To clarify the progress of the events under the beyond design basis events, it is necessary to evaluate the pressure toughness of containment vessel adequately. The containment vessel of fast reactor is composed of the various structures, and one of the thinnest boundary structures is bellows structure to absorb the thermal expansion of the coolant piping penetrating the containment vessel. In addition to the containment vessel boundary, evaluating the pressure toughness of reactor coolant and gas boundary is also important because of same reason of that in the containment vessel boundary. In the primary coolant and gas boundary, the cover gas bellows of the intermediate heat exchanger in fast reactor is one of the thinnest structures and has important role when the progress of the BDBE is considered. Therefore, in order to develop the evaluation method of the pressure toughness of bellows structure under the BDBE, the pressure failure tests and finite element analysis of the bellows structure subjected to internal pressure were performed in this study.
Yada, Hiroki; Ando, Masanori; Tsukimori, Kazuyuki; Ichimiya, Masakazu*; Anoda, Yoshinari*
Proceedings of 2016 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2016) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2016/07
no abstracts in English
Takaya, Shigeru; Fujisaki, Tatsuya*; Tanaka, Masaaki
Proceedings of 2016 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2016) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2016/07
JAEA is conducting R&D of an advanced loop-type sodium cooled fast reactor. The cooling system is planned to be simplified by employing a two-loop configuration and shortened piping with less elbows than Monju in order to reduce construction costs. The design increases flow velocity in the hot-leg piping and induces large flow turbulence around elbows. Therefore, flow-induced vibration is one of main concerns. The flow field in the hot-leg piping is affected by flow disturbance at the inlet, so it is important to evaluate flow field including the upper plenum. In this study, we analyzed unsteady fluid flow by using an integrated model of the upper plenum and the hot-leg piping system. Unsteady Reynolds averaged Navier-Stokes simulation with Reynolds stress model was used. In general, the simulation results obtained by using the integrated model show a similar tendency with the experiment results of 1/3 scaled-model of hot-leg piping with deflect flows. The coupling effect of swirling and deflected flows seems to be not significant although further investigation is needed.
Nishida, Akemi; Ebine, Noriya; Li, Y.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iwasaki, Akihisa*; Sawa, Naoki*; Matsubara, Shinichiro*; Kitamura, Seiji; Okamura, Shigeki*
no journal, ,
A fast reactor core consists of several hundred core elements, which are hexagonal flexible beams embedded at the lower support plate in a hexagonal arrangement, separated by small gaps, and immersed in a fluid. Core elements have no support for vertical fixing in order to avoid the influence of thermal expansion and swelling. These days, in Japan, larger earthquake vibrations are postulated in seismic evaluations. So, it is necessary to consider vertical displacements (rising) and horizontal displacements of the core elements simultaneously because vertical seismic vibrations are larger than the acceleration of gravity. The 3D vibration behavior is affected by the fluid force of the ambient coolant and contact with the surrounding core elements. In this study, single-model vibration tests using a full-scale test model were conducted, and the basic characteristics of 3D vibration behavior of the core element were examined. In addition, structures restricting vertical displacements (dashpot structure) were devised, and their effectiveness was verified. As a result of the tests, the effects of the ambient condition (in air, in static water, and in flowing water), gap between the pads, vibration directions, vibration waves, and dashpot structures on the vibration behavior of the core element were examined. As regards the ambient condition, the vertical displacements were larger in flowing water that simulates the coolant flow than in air and in static water, because of upward fluid force in flowing water. As regards the gap between the pads, the larger the gaps was, the stronger the interferences due to horizontal displacements, and the smaller the vertical displacements were. The dashpot structure was verified to be suitable for reducing vertical displacements.